[CtrlU] 성능 개선
1. 병목 지점 탐색 과정
Todo 도메인 API들의 성능 병목 가능성을 파악하기 위해 mock.sql, auth.http, todo.http 파일을 활용하여 사전 분석을 진행했다.

초기 분석 결과, GET /todos/within-24hours 쿼리가 약 500ms의 응답 시간을 기록하며 잠재적인 병목 지점으로 나타났다.
2. 로그를 사용한 문제 파악
/todos/within-24hours는 CRUD 형식의 간단한 로직이 아닌, 24시간 내 todo를 업로드한 친구들의 목록과, 그 친구들을 Green과 Gray로 나누는 작업까지 필요한 로직이다. 현재 코드에서는 로그는 아래와 같고, API는 한 번 호출되었지만 쿼리가 총 16번 호출된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
1) 회원 정보 조회
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.created_at,
u1_0.email,
u1_0.modified_at,
u1_0.nickname,
u1_0.password,
u1_0.profile_image_key,
u1_0.role,
u1_0.status,
u1_0.verify_token
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
and u1_0.status=?
2) 친구관계인 친구 목록 조회하기
Hibernate:
select
case
when f1_0.from_user_id=?
then f1_0.to_user_id
else f1_0.from_user_id
end
from
friendship f1_0
where
(
f1_0.from_user_id=?
or f1_0.to_user_id=?
)
and f1_0.status='ACCEPTED'
3) 24시간 내 할일 등록한 친구 조회(요청한 갯수만큼)
Hibernate:
SELECT
*
FROM
( SELECT
t.*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION
BY
t.user_id
ORDER BY
t.created_at DESC) AS rn
FROM
todo t
WHERE
t.user_id IN (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
AND t.created_at >= ?
AND t.status <> 'GIVEN_UP' ) ranked
WHERE
ranked.rn = 1
ORDER BY
ranked.created_at DESC
LIMIT
?
OFFSET
?
4) 전체 친구 갯수 구하기 (페이지 수를 구하기 위함)
Hibernate:
SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
( SELECT
user_id
FROM
todo
WHERE
user_id IN (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
AND created_at >= ?
AND status <> 'GIVEN_UP'
GROUP BY
user_id ) AS grouped
5) 친구 및 내 이미지 사진 가져오기 (11회 반복)
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.profile_image_key
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
...
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.profile_image_key
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
6) 나의 최신 할 일 존재 여부
Hibernate:
select
t1_0.id
from
todo t1_0
left join
user u1_0
on u1_0.id=t1_0.user_id
where
u1_0.id=?
and t1_0.created_at>?
and t1_0.status<>?
limit
?- 현재 코드에서 친구 및 내 프로필 이미지를 가져오기 위해 불필요한 쿼리가 총 11회 진행되고 있다. 앞에서 내 정보 조회 및 친구 정보 조회 시 같이 프로필 이미지까지 가져오게 하면 병목을 완화할 수 있을 것 같다.
- GREEN과 GRAY 상태의 친구를 분리하기 위해 stream을 두 번 사용하는 것은 비효율적이므로, Comparator를 사용하여 한 번의 정렬로 끝낼 수 있다.
3. 문제 해결
1. N+1 문제 해결
// 수정 전 코드
List<GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend> responseFriends = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : latestTodos) {
long friendId = todo.getUser().getId();
long latestTodoId = todo.getId();
String seenTodoIdStr = (String)redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(redisKey, String.valueOf(friendId));
long seenTodoId = seenTodoIdStr != null ? Long.parseLong(seenTodoIdStr) : -1;
GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status status = seenTodoId < latestTodoId
? GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GREEN
: GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GRAY;
String profileImage = userRepository.getImageById(friendId);
responseFriends.add(new GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend(
friendId,
awsS3Service.generateGetPresignedUrl(profileImage),
status
));
}
// 수정 후 코드
// N+1 해결: 친구 프로필 이미지 정보와 Redis의 '본상태' 정보를 한 번에 조회
List<Long> friendIds = latestTodos.stream()
.map(todo -> todo.getUser().getId())
.toList();
Map<Long, String> friendProfileImages = userRepository.findImageMapByIdIn(friendIds);
String redisKey = REDIS_KEY_PREFIX + userId;
List<String> friendIdStrings = friendIds.stream().map(String::valueOf).toList();
List<Object> seenTodoIdObjects = redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(redisKey, friendIdStrings);
Map<Long, Long> seenTodoMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < friendIds.size(); i++) {
if (seenTodoIdObjects.get(i) != null) {
seenTodoMap.put(friendIds.get(i), Long.parseLong((String) seenTodoIdObjects.get(i)));
}
}
// 루프 내에서는 조회 없이 Map에서 데이터를 가져와 가공만 함
List<GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend> responseFriends = latestTodos.stream().map(todo -> {
long friendId = todo.getUser().getId();
long latestTodoId = todo.getId();
long seenTodoId = seenTodoMap.getOrDefault(friendId, -1L);
GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status status = seenTodoId < latestTodoId
? GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GREEN
: GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GRAY;
String profileImage = friendProfileImages.get(friendId);
return new GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend(
friendId,
awsS3Service.generateGetPresignedUrl(profileImage),
status,
todo.getCreatedAt()
);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());각 todo마다 DB와 Redis에 접근하는 로직 대신, 처음에 각각 DB와 Redis(multiGet)에서 필요한 정보를 모두 조회한 후, 이를 바탕으로 반복문은 Map 가공만 하도록 수정하였다.
2. 복잡한 정렬 과정 단순화
//수정 전 코드
// 초록색 상태(GREEN)와 회색 상태(GRAY)를 나누고 GREEN이 먼저 오도록 정렬
List<GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend> greenFriends = responseFriends.stream()
.filter(f -> f.status() == GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GREEN)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend> grayFriends = responseFriends.stream()
.filter(f -> f.status() == GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GRAY)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// greenFriends 먼저, 그 뒤에 grayFriends 합침
greenFriends.addAll(grayFriends);
//수정 후 코드
// 최적화된 정렬: Comparator를 사용하여 한 번에 정렬
responseFriends.sort(Comparator
// 1차 정렬: GREEN 상태가 먼저 오도록 (GREEN=0, GRAY=1)
.comparing((GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend f) -> f.status() == GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Status.GREEN ? 0 : 1)
// 2차 정렬: 1차 정렬이 같을 경우, createdAt을 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
.thenComparing(GetRecentUploadFriendsResponse.Friend::createdAt, Comparator.reverseOrder()));
별도의 공간을 사용하지 않으며(in-place 정렬), 한 번의 작업으로 모든 정렬이 끝나도록 Comparator를 사용하였다.
4. 결과
기존에 작성해놓은 테스트코드 덕분에 리팩토링을 진행한 후에도 코드 로직에 문제가 없는지 빠르게 점검할 수 있었다.
1) 회원 정보 조회
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.created_at,
u1_0.email,
u1_0.modified_at,
u1_0.nickname,
u1_0.password,
u1_0.profile_image_key,
u1_0.role,
u1_0.status,
u1_0.verify_token
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
and u1_0.status=?
2) 친구 목록 조회
Hibernate:
select
case
when f1_0.from_user_id=?
then f1_0.to_user_id
else f1_0.from_user_id
end
from
friendship f1_0
where
(
f1_0.from_user_id=?
or f1_0.to_user_id=?
)
and f1_0.status='ACCEPTED'
3) 친구들의 가장 최근 할 일 조회
Hibernate:
SELECT
*
FROM
( SELECT
t.*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION
BY
t.user_id
ORDER BY
t.created_at DESC) AS rn
FROM
todo t
WHERE
t.user_id IN (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
AND t.created_at >= ?
AND t.status <> 'GIVEN_UP' ) ranked
WHERE
ranked.rn = 1
ORDER BY
ranked.created_at DESC
limit
?
4) Count 조회 쿼리
Hibernate:
SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
( SELECT
user_id
FROM
todo
WHERE
user_id IN (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
AND created_at >= ?
AND status <> 'GIVEN_UP'
GROUP BY
user_id ) AS grouped
5) 친구 프로필 일괄 조회
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.created_at,
u1_0.email,
u1_0.modified_at,
u1_0.nickname,
u1_0.password,
u1_0.profile_image_key,
u1_0.role,
u1_0.status,
u1_0.verify_token
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id in (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
6) 내 프로필 조회
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.profile_image_key
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
7) 내 최근 할일 조회
Hibernate:
select
t1_0.id
from
todo t1_0
left join
user u1_0
on u1_0.id=t1_0.user_id
where
u1_0.id=?
and t1_0.created_at>?
and t1_0.status<>?
limit
?
그 결과, 위와 같이 16개의 쿼리를 7개로 줄였다. 그리고 응답 시간은 아래와 같이 191ms로 줄였다.
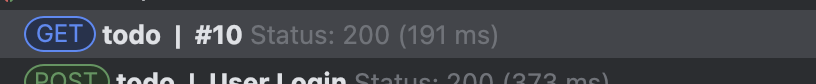
5. 추가 작업
쿼리를 최대한 줄이긴 했지만, 각 쿼리에 인덱스를 부여하지 않아 최대한 성능을 최적화했다고 볼 수 없다. 따라서 Profiler를 이용하여 각 코드 라인 중 성능이 좋지 않는 코드 라인을 조회하였다.
1. Projection 적용

현재 친구 프로필을 일괄 조회할 때, 필요한 정보는 id와 profileImage 뿐이지만 모든 정보를 조회하고 있다. 따라서 Projection을 이용하여 필요한 정보만 조회하도록 수정하였다.
public interface UserImageProjection {
Long getId();
String getProfileImageKey();
}그 결과 다음과 같이 필요한 정보만 조회해오는 것을 알 수 있다.
//수정 전
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.created_at,
u1_0.email,
u1_0.modified_at,
u1_0.nickname,
u1_0.password,
u1_0.profile_image_key,
u1_0.role,
u1_0.status,
u1_0.verify_token
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id in (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
//수정 후
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.profile_image_key
from
user u1_0
where
u1_0.id in (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)2. 인덱스 적용

친구의 최근 할 일을 조회하는 쿼리에서 많은 병목이 생기고 있다. 쿼리는 다음과 같다.
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT
t.*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY t.user_id ORDER BY t.created_at DESC) AS rn
FROM
todo t
WHERE
t.user_id IN (994, 593, 915, 771, 856, 317, 888, 959, 654, 867)
AND t.created_at >= '2025-08-27 17:47:43'
AND t.status <> 'GIVEN_UP'
) ranked
WHERE
ranked.rn = 1
ORDER BY
ranked.created_at DESC;EXPLAIN 결과 다음과 같다.

실행 계획의 두 번째 줄(id: 2)이 가장 핵심적인 문제입니다.
- type: ALL (Full Table Scan)
- todo 테이블의 데이터를 찾기 위해, 테이블의 모든 행(약 49만 5천 개)을 처음부터 끝까지 전부 읽고 있다.
- Extra: Using filesort
- ORDER BY를 처리하기 위해 인덱스를 사용하지 못하고, 메모리나 디스크를 사용하여 별도의 느린 정렬 작업을 수행했다.
현재 쿼리에서 todo 테이블에서 userId를 기준으로 조회를 하고 각 userId에 따라 createAt을 기준으로 todo를 조회하고 있다. 따라서 다음과 같은 복합 인덱스를 추가하였다.
CREATE INDEX idx_todo_user_id_created_at ON todo (user_id, created_at DESC);그 결과 다음과 같이 최적화 되었다.

응답 시간은 다음과 같이 191ms -> 96ms로 감소하였다.
